k3s
Lightweight Kubernetes
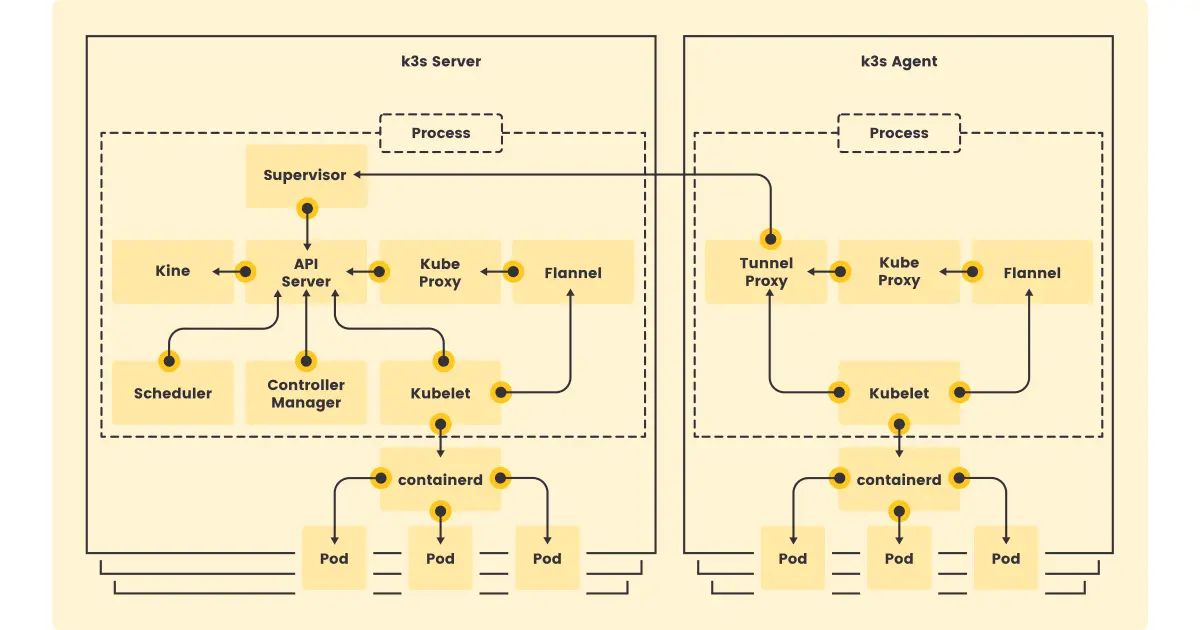
How it Works
The above figure shows the difference between K3s server and K3s agent nodes. For more information, see the architecture documentation.
install k3s
K3s provides an installation script that is a convenient way to install it as a service on systemd or openrc based systems. This script is available at https://get.k3s.io. To install K3s using this method, just run:
1
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -
After running this installation:
The K3s service will be configured to automatically restart after node reboots or if the process crashes or is killed
A kubeconfig file will be written to /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml
A single-node server installation is a fully-functional Kubernetes cluster, including all the datastore, control-plane, kubelet, and container runtime components necessary to host workload pods. It is not necessary to add additional server or agents nodes, but you may want to do so to add additional capacity or redundancy to your cluster.
install kubectl
Download the latest release with the command
1
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
Install kubectl
1
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
check kubectl is installed
1
kubectl version --client
install helm
1
2
3
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
Cluster Access
The kubeconfig file stored at /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml is used to configure access to the Kubernetes cluster. If you have installed upstream Kubernetes command line tools such as kubectl or helm you will need to configure them with the correct kubeconfig path. This can be done by either exporting the KUBECONFIG environment variable or by invoking the --kubeconfig command line flag. Refer to the examples below for details.
Leverage the KUBECONFIG environment variable:
1
2
3
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
helm ls --all-namespaces
Or specify the location of the kubeconfig file in the command:
1
2
kubectl --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml get pods --all-namespaces
helm --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml ls --all-namespaces
Accessing the Cluster from Outside with kubectl Copy /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml on your machine located outside the cluster as ~/.kube/config. Then replace the value of the server field with the IP or name of your K3s server. kubectl can now manage your K3s cluster.